zur deutschen Version, Flagge klicken oder tippen

- parliamentaric monarchy with the British monarch as chief of state
- zone of US-american influence
• Flags
• historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National flag,
ratio = 3:5,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4






Merchant flag and official flag at sea,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)




Naval flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)




since 1974(?),
Flag of the Governor General,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World, kemlu.go.id




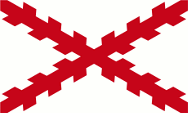
16th/17th century,
The island belongs to the Spanish sphere of influence,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




1649–1762,
Flag of France,
Source: Sodacan [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons



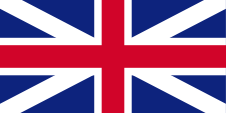
1762–1801,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Die Welt der Flaggen






1801–1967,
Union Flag → quasi national flag,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)





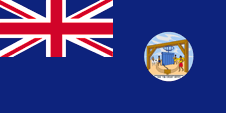
1875–1903,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1882–1903,
Flag of the Administrator(?),
ratio = 1:2



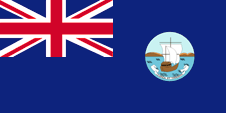
1903–1967,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1903–1967,
Flag of the Administrator,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1967–1974,
National and state flag,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1967–1974,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



Windward Islands (1838–1958):

1903–1958, doubtful,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1885–1960,
Flag of the Governor-in-Chief,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



Federation of the West Indies (1958–1962):
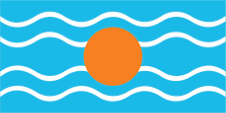
Flag of the Federation of the West Indies,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Governor General,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




The current flag of Grenada was introduced on 7th of February in 1974. It shows
four triangles in green and yellow, surrounded by a red border. In the centre is
a yellow star on a red disc, and six more in the red border. The seven stars
symbolise the seven administrative districts of the island. In the green
triangle on the mast side is placed a nutmeg, the island's most important
export. The colour combination of green, yellow and red in the today's flag are
the Pan-African colours: around 1900, the Pan-African movement began, which
wanted to emphasise the commonalities of all people with black skin. The colour
triad green-yellow-red, which many African states adopted in their flags after
gaining independence, stands for the political unity of Africa. The first
country to do so was Ghana in 1957, and the colours of Ethiopia (Abyssinia), the
oldest independent state in Africa, are considered to be the origin.
As
the country appears to follow the British ensign and colour system, the colours
of the flag will correspond to the spectrum given by the British Ministry of
Defence in its publication "Flags of all Nations" (a service regulation) for the
following colours: Green = pt 348 c, Red = pt 186 c, Deep Yellow = pt 116 c.
Grenada still uses the British Ensign system to this day. This points to the
links with United Kingdom, as the naval flag is a white ensign, a white flag
with a continuous red St George's cross and with the national flag in the upper
corner.
From the time, the territory became a British possession,
individuals, citizens and also the authorities represented their status as
citizens or organs of the British nation, embodied in the United Kingdom,
through the use of the Union Jack, also called the "Union Flag". At sea, the
British merchant flag, the Red Ensign, was intended for British citizens from
1864. In a few cases, the citizens of a colony were authorised by the British
Admiralty to use their own Red Ensign with the colony's badge at sea. The Union
Jack in the top corner of these flags signalled the connections to United
Kingdom.
Grenada originally belonged to the British colony of the
Windward Islands, later to the Federation of the West Indies and became a
dissociated own colony in 1962.
United Kingdom introduced a flag system
in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white
flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack
in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign"
(also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag
with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
•
governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment →
the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff
quadrant of the flag.
From 1865, the ships of the colonial governments
were allowed to use a Blue Ensign with a badge at the flying end. The respective
governments were to provide appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring
privateers from colonies were only allowed to use a Red Ensign with a badge if
the British Admiralty had issued a corresponding licence for that colony.
Such a badge was often a regional landscape depiction on a disc, often
showed ships, historical events or could simply be a kind of logo. Very often a
badge also contained the name of the country or a motto. However, some
possessions had a coat of arms from the beginning or were given their own coat
of arms over the years and the badge was abolished. To ensure a largely uniform
appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were
displayed on a white disc in the size of the former badges.
However,
there were also exceptions, as some colonies dispensed with this white disc and
placed their coat of arms or even just the shield – sometimes enlarged –
directly on the bunting. As early as the 1940s, the white disc was removed and
the coat of arms was applied directly or enlarged. This conversion process took
place gradually, nowhere simultaneously and completely. In some British
possessions flags with the white disc are still in use today, in others no
longer and in some areas both variants exist side by side.
From 1834 to
1960, the area was part of the British colony of the Windward Islands, a federal
colony consisting of individual sub-areas, sub-colonies or islands. These
individual colonies had their own flags, also called "Blue Ensigns" with their
own badge, for use by the governments of these colonies. The overarching
political entity of the British Windward Islands most likely did not have an
additional Blue Ensign of its own, but its own badge. This badge was created in
1886 and showed an heraldic shield divided into four parts with the colours red,
yellow, green and white, surrounded by a white belt with the inscription
"Governor in Chief, Windward Islands", with the British crown above. Below is a
white banner with the motto of the islands: "i pede fausto" → "Walk with a
blessed foot". In 1903, the design of the crown was changed slightly (to the
Tudor crown). The Governor of Barbados was always also the Governor-in-Chief of
the colony of the British Windward Islands. The Governor-in-Chief used the
Windward Islands badge on his flag after all. He was represented locally by a
governor in the associated sub-territory, sub-colony or island. The federal
colony ceased to exist when it was incorporated into the Federation of the West
Indies, led by a Governor-General. Locally, in the associated sub-territory,
sub-colony or island, the highest representative of the Crown retained his rank.
He remained an administrator or governor. The local flags (e.g. blue or red
ensigns, i.e. separate state or merchant flags) have been retained.
Grenada received its own badge in 1875. It showed on a disc a sugar mill driven
by an oxen galley and some farm workers. The island's motto at that time
appeared below: "Hae tibi erunt artes" → "These arts will be yours". Between
1903 and 1967, the badge showed a ship travelling towards the coast. Below, on a
banner, was the island's motto at that time: "Clarior e tanebris" → "I shine
more brightly from the darkness". In 1875, an own "Blue Ensign" was also
introduced as the state flag at sea, a dark blue bunting with a flag depiction –
the British Union Jack – in the upper corner, which showed the badge in the
flying end of the flag.
From 1958 to 1962 the territory was also part of
the British colony "Federation of the West Indies". This political project was
an attempt to unify the administration and to create a state modelled on Canada,
but also to counteract the independence efforts of the associated islands and
colonies. However, jealousies arose between the large and small islands and even
led to open dispute. The flag of the "Federation of the West Indies" was a light
blue flag with four horizontal white wavy lines and a golden disc in the middle.
It symbolized the sun over the Caribbean Sea. There is some doubt about the
color of the blue; it is often assumed to be the usual British heraldry blue.
However, a contemporary description calls it an "imperial blue" which would be
light blue and many contemporary prints also show this light blue.
On 3rd
of March in 1967, internal self-government was granted by United Kingdom and
Grenada became an autonomous state associated with United Kingdom. In this
context, a flag was introduced which ended the tradition of the "Ensigns". It
was horizontally striped blue-yellow-green with a nutmeg on a large oval in the
centre. This flag had already been adopted on 19th of January in 1967. Its
colours were also used by other members of the Federation of the West Indies,
albeit in different combinations. Independence was granted by United Kingdom on
7th of February in 1974. In this context, the today's flag was introduced.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (D), Flags of the World


1875–1903,
Badge,
Source, by:
Flags of the World

1903–1974,
Badge,
Source, by:
Flags of the World

since 1974,
Coat of arms of Grenada,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4

Grenada received its own badge in 1875. It showed on a disc a sugar mill driven by an oxen galley and some farm workers. The island's motto at that time appeared below: "Hae tibi erunt artes" → "These arts will be yours". Between 1903 and 1967, the badge showed a ship travelling towards the coast. Below, on a banner, was the island's motto at that time: "Clarior e tanebris" → "I shine more brightly from the darkness". The coat of arms of the state was like the flag introduced on 7th of February in 1974. The blazon is squared by a yellow cross. From them are two red coloured with a golden leopard (→ England), and the other both are green with a white Mary-lily on a golden crescent. On the shield a golden helmet, a red-white torus as soon as red roses. Shield-holders are an armadillo on the right and a blue pigeon to the left. The pedestal of the coat of arms is green with a pond, a banana-palm-tree, a corn-plant and yellow blossoms.
Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Wikipedia (D), Flags of the World

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
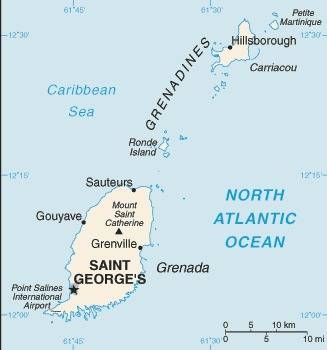
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 133 square miles
Inhabitants: 112.000 (2019), thereof 82% of African descent, 13% Mulattos, 2% Indians, 1% Europeans
Religions: 49% Protestant, 36% Roman Catholic, 5% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 843 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: St. George's, 7.000 inh.
official Language: English
other Languages: Creole English, Creole French
Currency: East Caribbean Dollar (EC$; XCD) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT – 4 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
CIA World Factbook

1498 · discovered
1650 · France purchases Grenada from private ownership
1762 · British capture
1779–1783 · French occupation
1833 · end of the slavery
1834–1960 · part of the British Colony of the Windward Islands
1958–1962 · part of the British Colony of the "Federation of the West Indies"
1967 · granting of internal self government
1974 · United Kingdom grants independence
1979 · Maurice Bishop becomes prime minister and extends the dealings to Cuba
1983 · coup d'état, murder of Maurice Bishop, military intervention of the USA under help of Caribbean auxiliary troops, enduring occupation of the island
1984 · elections
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
Discovery '97

When Columbus discovered the island in 1498, he named the island "Concepción". At some point in time the name "Grenada" came into use, but the origin of the name is unknown. It is believed that the island got its name from Spanish sailors of the 16th century to recall the city of Granada.
Source:
Wikipedia (D)


![]()











































