zur deutschen Version, Flagge klicken oder tippen

- Anguilla
- possession of the United Kingdom
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

since 1801,
Union Flag → quasi national flag,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)






since 1999,
National and state flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
Corel Draw 4






since 1864,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of all Nations






since 1988,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World





1958–1967, St. Kitts/Nevis & Anguilla,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1967, St. Kitts/Nevis & Anguilla,
National and state flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1967–1980,
National and state flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World,
Corel Draw 4




1967–1990,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
Corel Draw 4




1980–1990,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)






1990–1999,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: World Statesmen




1990–1999,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World



Leeward Islands (1833–1958):
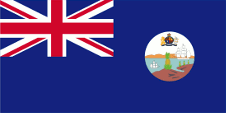
1871–1958,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1874–1959,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Wikipedia (EN)



Federation of the West Indies (1958–1962):
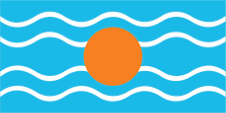
Flag of the Federation of the West Indies,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Governor General,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




Anguilla had been an English possession since 1650, and a British colony since
1801, so that the flag of United Kingdom had flown over the island since that
year. On land, and until 1864 also at sea, individuals, citizens and also the
authorities represented their status as citizens or bodies of the United Kingdom
by using the Union Jack, known as the "Union Flag". This means that on land, the
Union Flag is the national and state flag.
On land, the "Blue Ensign"
(actually the state flag at sea) with the country's badge/coat of arms may also
be used as the national flag for decorative purposes if the governor has
authorised this, for a limited period of time, e.g. at an event (including
outside the country) or for differentiation purposes if the use of the Union
Flag would be inappropriate or likely to cause confusion. On land, however, the
aspect ratio of the flag should be 3:5. A "Blue Ensign" is a dark blue baunting
with a representation of a flag – the British Union Jack – in the upper corner
and the country's badge in the flying end of the flag. The Union Jack emphasises
the links with United Kingdom.
United Kingdom introduced a flag system in
1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag
often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in
the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign"
(also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag
with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
•
governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment →
the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff
quadrant of the flag.
From 1865, the ships of the colonial governments
were allowed to use a Blue Ensign with a badge at the flying end. The respective
governments were to provide appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring
privateers from colonies were only allowed to use a Red Ensign with a badge if
the British Admiralty had issued a corresponding licence for that colony.
Such a badge was often a regional landscape depiction on a disc, often
showed ships, historical events or could simply be a kind of logo. Very often a
badge also contained the name of the country or a motto. However, some
possessions had a coat of arms from the beginning or were given their own coat
of arms over the years and the badge was abolished. To ensure a largely uniform
appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were
displayed on a white disc in the size of the former badges.
However,
there were also exceptions, as some colonies dispensed with this white disc and
placed their coat of arms or even just the shield – sometimes enlarged –
directly on the bunting. As early as the 1940s, the white disc was removed and
the coat of arms was applied directly or enlarged. This conversion process took
place gradually, nowhere simultaneously and completely. In some British
possessions flags with the white disc are still in use today, in others no
longer and in some areas both variants exist side by side.
From 1832 to
1958, the area was – from 1882 together with St. Kitts and Nevis – part of the
British colony of the Leeward Islands, a federal colony consisting of individual
sub-areas, sub-colonies or islands. These individual colonies had their own
flags, also called "Blue Ensigns" with their own badge, for use by the
governments of these colonies. The overarching political entity of the British
Leeward Islands also had its own Blue Ensign with its own Leeward Islands badge.
This badge was created in 1871 and showed a pineapple on a coastline with two
ships. The governor also used it on his flag. He was represented locally, in the
associated sub-territory, sub-colony or island, by an administrator.
The
federal colony ceased to exist when it was incorporated into the Federation of
the West Indies, led by a Governor-General. Locally, in the associated
sub-territory, sub-colony or island, the highest representative of the Crown
retained his rank. He remained an administrator or even governor. The local
flags (e.g. blue or red ensigns, i.e. separate state or merchant flags) have
been retained.
From 1958 to 1962 the territory was also – together with
St. Kitts and Nevis – part of the British colony "Federation of the West
Indies". This political project was an attempt to unify the administration and
to create a state modelled on Canada, but also to counteract the independence
efforts of the associated islands and colonies. However, jealousies arose
between the large and small islands and even led to open dispute. The flag of
the "Federation of the West Indies" was a light blue flag with four horizontal
white wavy lines and a golden disc in the middle. It symbolized the sun over the
Caribbean Sea. There is some doubt about the color of the blue; it is often
assumed to be the usual British heraldry blue. However, a contemporary
description calls it an "imperial blue" which would be light blue and many
contemporary prints also show this light blue.
The history of Anguilla
and also the flags used in the past were closely linked to St. Kitts and Nevis,
starting as early as 1816. United Kingdom granted St. Kitts, Nevis and Anguilla
internal self-government (autonomy as a state associated with United Kingdom) in
1967. In Anguilla, the idea of secession immediately came to life, which was
consistently implemented and Anguilla separated from St. Kitts and Nevis just in
1967. A flag with three dolphins, modified from the image on the escutcheon,
played a major role in this. The self-government that was granted led to chaos,
so that the island had to be placed under British administration again in 1971.
It was not until 1980 that the only de jure connection with St. Kitts and Nevis
officially ended.
Anguilla already had its own badge during its time
together with St. Kitts and Nevis. It showed a native with his boat on the
coast. Probably in 1958, a common heraldic shield was created for St. Kitts,
Nevis and Anguilla that combined the symbolism of the individual islands. It
showed Columbus with a telescope on board a ship (St. Kitts), three virgins at a
spring (Nevis) and a native with his boat on a coast (Anguilla). Also in 1958,
an own "Blue Ensign" was introduced for St. Kitts, Nevis and Anguilla as the
state flag at sea, a dark blue bunting with a flag depiction – the British Union
Jack – in the upper corner, which showed the shield on a white disc in the
flying end of the flag.
On 27th of February in 1967, St. Kitts, Nevis and
Anguilla were granted internal self-government by United Kingdom, and the
country became an autonomous state associated with United Kingdom. In this
context, a new flag was introduced. This flag showed three vertical stripes in
green, yellow and blue, and in the centre of the yellow stripe a black palm tree
with three branches (St. Kitts, Nevis and Anguilla).
In the same year,
Anguilla separated from St. Kitts, Nevis and introduced the dolphin flag. Its
design repeats the image of the shield introduced in 1980: three orange dolphins
combined in a circle on white over a narrow light blue field. The three dolphins
symbolise friendship, knowledge and strength. The circle of dolphins represents
continuity and the light blue field symbolises the sea. It was not until 1990
that an own "Blue Ensign" was introduced for Anguilla as the state flag at sea,
showing the heraldic shield in the flying end of the flag, which on the flag was
modified and enlarged again in 1999.
Source: Flags of the World,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Enzyklopädie,
Volker Preuß


to 1958,
Badge (Emblem) of Anguilla,
Source, by: Flags of the World

1958–1967,
Saint Christopher, Nevis and Anguilla,
Badge (Emblem) of Saint Christopher, Nevis and Anguilla,
Source, by: Flags of the World

since 1980,
Coat of arms of Anguilla,
Source, by: World Statesmen

Anguilla already had its own badge during its time together with St Kitts and
Nevis. It showed a native with his boat on the coast. Probably in 1958, a common
shield was created for St Kitts, Nevis and Anguilla, which combined the
symbolism of the individual islands. It showed Columbus with a telescope on
board a ship (St Kitts), three virgins at a spring (Nevis) and a native with his
boat on a coast (Anguilla). A coat of arms was introduced in 1980. It shows
three orange-coloured dolphins combined in a circle on white above a narrow
light blue field. The three dolphins symbolise friendship, knowledge and
strength. The dolphin circle represents continuity and the light blue field
symbolises the sea.
Source: Wikipedia (D),
Flaggen Enzyklopädie

Location:
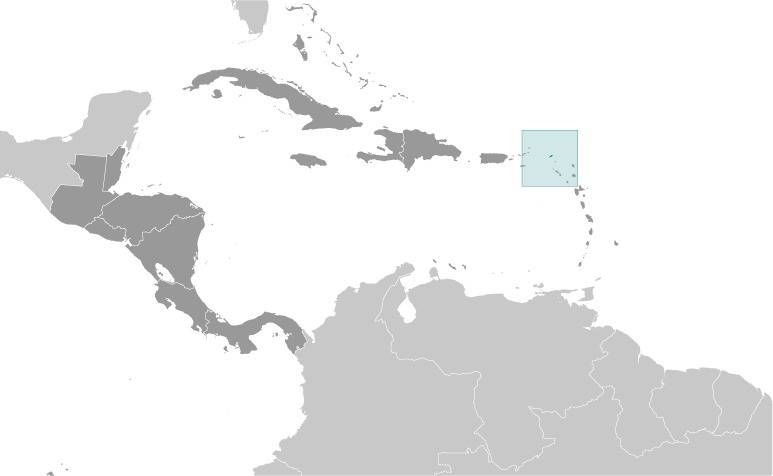
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
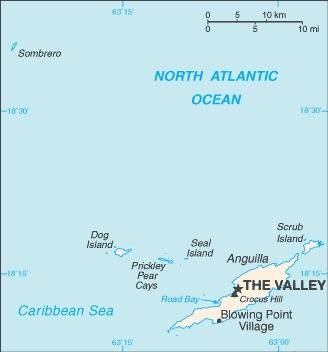
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 37 square miles
Inhabitants: 13.600 (2011), thereof 85.3% African/Black, 4.9% Hispanic, 3.8% mixed, 3.2% White
Religions: 73% Protestant, 7% Roman Catholic, 11% other Christian, 4% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 367 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: The Valley, 1.300 inh. (2011)
official Language: English
Currency: East Caribbean Dollar (XCD, EC-$) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT – 4 h
Source: Wikipedia (D),
CIA World Factbook

1493 · the Spanish seafarer Christoph Columbus discovers the island and names it Isla de Anguila, the island becomes a Spanish possession but was not colonized
1650 · appropriation of Anguilla by England
1696–1816 · part of the British Leeward Islands Colony
1745 · repulse of a French invasion
1796 · repulse of a French invasion
1816 · the Leeward Islands Colony becomes dissolved, St. Kitts becomes fused with Anguilla, Nevis and the Virgin Islands
1833 · re-estbalishment of the Leeward Islands Colony, to 1960 part of the British Leeward Islands
1882 · the British possessions of St. Kitts, Nevis and Anguilla become fused within the Leeward Islands Colony (Colony of St. Kitts, Nevis and Anguilla)
1958–1962 · part of the British colony "Federation of the West Indies"
27th of February 1967 · United Kingdom grants St. Kitts, Nevis and Anguilla interior self administration (autonomy as with Great Britain associated state)
1967–1969 · demands for independence on Anguilla
1971 · Anguilla becomes subordinated under the British administration again
1980 · Anguilla becomes separated from St. Kitts/Nevis and becomes a self-contained colony
Source: Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen

As columbus in 1493 discovered island he named it "Isla de Anguila" (Eel Island). Possibly he spoted eels here, which visited their spawn places.
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen


![]()
























![]()



![]()

![]()



![]()


![]()
![]()
![]()









