zur deutschen Version, Flagge klicken oder tippen

- federal elective monarchy with parliamentary approaches
- own name: Daulat Al-Imarat al-Arabiya al-Muttahida
- former names: Pirate Coast, Trucial Oman, Trucial States
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• The Emirates
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National, state and merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World, Wikipedia (EN)






since ca. 1980,
alternative Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (EN)




Flag of the Armed Forces,
ratio = 7:10 (?),
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Army,
ratio = 7:10 (?),
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Air Force,
ratio = 7:10 (?),
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Navy,
ratio = 7:10 (?),
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Head of State,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World





to 1820, Ghafiri & Hinawi, in:,
Abu Dhabi, Umm Al Quwain, Ajman
Source, by: Flags of the World




to 1820, Al-Qawasim, in:,
Ras Al Khaimah,
Source: Limghadar, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons




1820–ca.1936, "The White Pierced Red",
Flag of the maritime peace treaty,
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1820–ca.1971, in practice,
Flag of the maritime peace treaty,
ratio = 1:2 & 1:3...,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1892–1971,
Union Flag → quasi state flag,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)






ca.1936–1971, in practice,
Flag of the maritime peace treaty,
ratio = 1:2 & 1:3...,
Source, by: Flags of the World, Flaggenbuch 1939



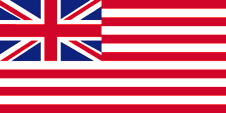
1822–1971,
Flag of the British Persian Gulf Residency,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




1968–1971,
Flag of the Trucial States Council,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1973–2008,
Flag of the Head of State,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




The flag of the United Arab Emirates was officially introduced on 2nd of December on 1971 in connection with the country's independence from United Kingdom. It shows three horizontal stripes in green, white and black and a vertical red stripe on the pole. The width of the red stripe is variously specified as one third or half the height of the flag. Officially, the colours of the flag have the following meanings: Green stands for fertility and prosperity, white for peace and honesty, black for solidarity and mental strength, red for resilience and bravery. But these explanations are also offered: Red is the colour that the flags of the individual emirates have in common, green stands for fertility, white for neutrality and black for the oil to which the country owes its prosperity. The hues of the colours of the flag appear to have been defined, also in the Pantone colour space: green = Pantone 348 C and red = Pantone 186 C.
The colour quadradure of green, white, black and red is a specifically Arabic color symbol, the Pan-Arabian colors. The (pan)Arab colors were officially introduced as the colours of the Arab movement during the First World War, when the Kingdom of Hejaz broke away from the Ottoman Empire, by Sherif Hussein of Mecca – from the Hashemid dynasty. The flag of the Hejaz served as a template. The colors have the following meaning: Red is the color of Omar, the second caliph. White represents the Umayyads, a caliph dynasty that dates back to the fifth caliph Moawija I. Green represents the Fatimids, an Ismaili-Shiite caliph dynasty that dates back to the fourth caliph Ali. Black represents the Abbasids, a caliph dynasty that dates back to Caliph Abbas I. Red is also the color of the Hashemids, an Arab ruling dynasty that probably goes back to Hashim ibn Abd al-Manaf, Muhammad's grandfather. Green is also the color of Islam in general, and therefore does not only refer to the Arab countries.
The head of state of the UAE, known as "President", is elected every five years by the Supreme Ruling Council of the seven emirates. He is de facto always the acting Emir of Abu Dhabi. He has his own flag. It shows the design of the UAE national flag, but bears the UAE coat of arms in the centre of the white stripe.
The history of the country begins with the piracy of Arab tribes, who were able to develop into very successful pirates in the region due to the confrontation between the major naval powers in the Napoleonic Wars and the recovery in world trade after Napoleon's defeat. The most important representatives of piracy were the tribal organisations of the Hinawi (Sheikdom of Abu Dhabi, later also Dubai and Fujairah) and of the Ghafiri (in the sheikhdoms of Umm Al Quwain and Ajman) and the powerful Al-Qawasim dynasty, which ruled in the emirate of Ras Al Khaimah and later in Sharjah too. The Hinawi and Ghafiri used single-coloured red flags without defined side lengths. The Al-Qawasim, as a powerful naval power, already had a more modern flag. It was horizontally striped green-white-red with an Arabic inscription in the centre "Nassr min Allah wa fatah karib" → "By Allah to victory and total subjugation". United Kingdom, as the major naval power, decided to take military action against piracy and defeated the Arab tribes of the region, who were forced to sign a maritime peace treaty in 1820 to end piracy. The Arabs were bound to peace, but their ships were given freedom of movement in trade and were allowed to call at British harbours unhindered. To do so, however, they had to use the treaty flag of the maritime peace treaty on land and at sea, the "White Pierced Red" used in the British navy, apparently a previous square signalling flag. It was square white with a red square in the centre, one-ninth the size of the total area of the flag. However, in times of war, all signatories were allowed to revert to their previous flags. In addition, the entire region was placed under indirect British colonial administration in 1822 through the British Persian Gulf Residency, which existed until 1971 and was under the colonial administration of India until its independence. The flag of the Persian Gulf Residency was allegedly the flag of the East India Company, which was disempowered in 1858 and also had branches in the region, for example in Gombroon (Bandar Abbas), Muscat and Basra. The flag was probably simply retained. Although the peace treaty of 1820 was only a treaty document, a new territorial term came into use for the territory of the pacified Arabs from 1853, usually called "Trucial Oman", "Trucial Coast" or "Trucial States", which was entered on maps, for example. The treaty flag, the "White Pierced Red", was not very popular with the pacified Arabs, and when it was used, its shape was changed to an elongated form common in the region. However, the Al-Qawasim adopted the design as the flag of their emirates and it is still used there today. With the peace treaty, the competing Hinawi and Ghafiri sheikhs saw the Al-Qawasim as being more responsible than themselves. Over the years, it became clear to the sheikhs that they had to use the same flag as the Al-Qawasim, or even had to adopt their flag. For this reason, Abu Dhabi even briefly returned to the single-coloured red flag in 1833, until a single-coloured red flag with a white stripe on the mast became established as the treaty flag for the Hinawi and Ghafiri, just as it was then and is now used by Bahrain and Qatar (perhaps modelled on them) and as it is still used today by Ajman and Dubai. The British administration renewed the peace treaty in 1834 and 1853 ("Perpetual Maritime Truce"). The old flag, which was permitted under the maritime peace treaty in the event of war, could have been used until 1892, because in that year United Kingdom established its protectorate and took over the foreign and defence policy of the contracting states. This meant that the British "Union Jack" was used in the administration, but private ships were also allowed to use it. United Kingdom raised the peace treaty to a new constitutional level in 1952 when the Trucial States Council was created, which existed until independence in 1971 and also had its own flag from 1968. This had three horizontal stripes in red, white and red in a ratio of 1:2:1, with a green seven-pointed star in the centre of the broad white stripe. Its rays stood for the seven emirates in the Council. Nine were originally planned, but Qatar and Bahrain did not join. Otherwise, the contract flags continued to be used until 1971, with the single-colour red banners sometimes still being used on land, e.g. in Fujairah. Allegedly there was also a common naval flag and a common war flag for the council.
Source:
UAE Forsan,
Wikipedia (EN),
Flags of the World,
Volker Preuß


since 22nd of March in 2008,
Coat of arms of United Arab Emirates,
Source: Wikipedia (EN), Corel Draw 4

1973–2008,
Coat of arms of United Arab Emirates,
Source: Wikipedia (EN), Corel Draw 4

The coat of arms of the state was introduced in 1973. It shows a golden-silver falcon, the emblem of the Quraish tribe. Until 2008, the eagle wore a red round breast shield surrounded by an eight-link chain. The shield showed a dhow, a traditional Arab sailing ship. It was probably modelled on the coats of arms of Abu Dhabi and Dubai. The eight-link chain symbolised the seven members of the federation and Qatar, which did not join the federation in the end. The falcon holds a red ribbon with the name of the state in its talons. A new coat of arms was introduced on 22nd of March in 2008. The dhow was removed and replaced by an image of the national flag. The chain was also removed and replaced by a white ribbon with seven white stars. The falcon has also had seven tail feathers since 1973.
Source: Wikipedia (EN), Flaggen Wappen Hymnen


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
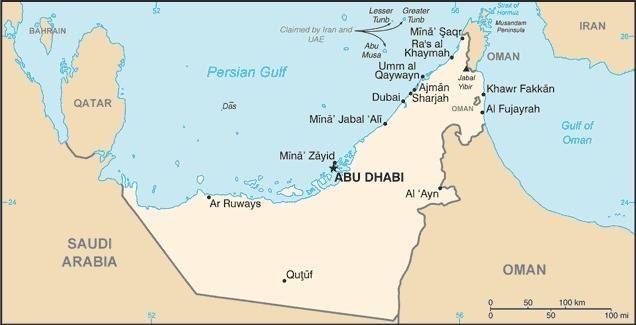
Source: CIA World Factbook

Source: by UAE_en-map.png: Chumwa [CC-BY-SA-3.0 or GFDL], via Wikimedia Commons

– Abu Dhabi
– Ajman
· Manama
– Dubai
– Fujairah
– Ras Al Khaimah
– Umm Al Quwain
– Sharjah
· Hira
· Kalba
· Daba
· Hamriyya
· Khor Fakkan

Area: 32.278 square miles
Inhabitants: 9.558.000 (2021), thereof (10 % citizens), thereof 70 % Arabs, 20 % Indians and Pakistani, 5% Persian, 4% Filipinos, 2,5% Europeans
Religions of the citizens: 96 % Muslim
Density of Population: 296 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Abu Dhabi, 1.450.000 inh. (2018)
official Language: Arabisch
other Languages: English, Hindi, Urdu, Farsi
Currency: 1 VAE-Dirham (Dh., AED) = 100 Fils
Time Zone: GMT + 4 h
Source: Wikipedia (DE)

4th millennium B.C. · first settlement
ca. 1st millennium B.C. · settlement by Arabs
4th to 7th century A.D. · the area of the today's emirates belongs to the Persian Sassanid Empire
630 · introduction of Islam
632 · apostasy
634 · the area of the today's emirates is conquered by the Arab Caliphate, re-Islamization
middle ages · the area of the today's emirates belongs to Oman
16th century · military and commercial operations of the Portuguese
ca. 1650 · under the control of the Ottoman Empire
ca. 1750 · conquest by Bedouins, Beginning of piracy, the area is called "Pirate Coast", establishing the Emirate of Ras Al Khaimah by the Qawasim Clan of the Huwayla Tribe, establishing of the Emirate of Ajman by the Al Nuaimi
1761 · establishing of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi by the the Banu Yas
1765 · the Emirate of Ras Al Khaimah acquires the town of Khor Fakkan from Persia
1775 · establishing of the Emirate of Umm Al Quwain by the Al Mualla Family of the Al Ali Clan
1806–1819 · actions of the British navy against the pirates
1820 · peace treaty for the end of piracy
1833 · establishing of the Emirate of Dubai as a separation from Abu Dhabi by the Al Abu Falasa lineage under leadership of the Al Maktoum Family
1834 · renewal of the peace treaty
1853 · renewal of the peace treaty, "Perpetual Maritime Truce", the area is now called "Trucial Oman" or "Trucial States"
1869 · death of Sultan ibn Saqr of Ras Al Khaimah, division by heritage, establishing of the Emirate of Sharjah (incl. Khor Fakkan)
1871 · establishing of the Emirate of Daba (Dibba) as a separation from Sharjah
1875 · establishing of the Emirate of Hamriyya as a separation from Sharjah
1876 · in the to Sharjah belonging Fujairah begins the reign of the ash-Sharqi clan
1892 · United Kingdom establishes its protectorate over the emirates
1900–1921 · Ras Al Khaimah and Sharjah are temporarily reunited
1902 · Fujairah declares its independence from Sharjah
1903 · establishing of the Emirate of Kalba as a separation from Sharjah
1915 · establishing of the Emirate Hira as a separation from Sharjah
1922 · the Emirate of Hamriyya beomes re-incorporated to Sharjah
1939 · establishment of a British resident of the Trucial States, seat: Dubai
1942 · the Emirate of Hira beomes re-incorporated to Sharjah
1951 · the Emirate of Daba beomes re-incorporated to Sharjah
1952 · the Emirate of Kalba beomes re-incorporated to Sharjah
1952 · formation of the Trucial Council under British sovereignty, border disputes with Saudi Arabia, the point of conflict: Bureimi Oases
1962 · first oil exports
1971 · drafting of a constitution for an union between Abu Dhabi and Dubai, with the planned accession of all emirates
2nd of December 1971 · United Kingdom grants independence to the emirates, establishing of the United Arab Emirates (Abu Dhabi, Ajman, Fujairah, Sharjah, Dubai and Umm Al Quwain)
10th of February · accession of Ras Al Khaimah
1999 · fixing of the border with Saudi Arabia
Source:
Wikipedia (DE),
World Statesmen,
Discovery '97,
Volker Preuß

The country had the name "Pirate Coast" up to its pacification by the maritime peace treaty with United Kingdom in 1853, then "Trucial Oman" or "Trucial States". On the occasion of independence was adopted in 1971 the today's name.
Source: Volker Preuß


![]()






















































