zur deutschen Version, Flagge klicken oder tippen

- Republic of Slovenia
- parliamentary republic
- own name: Republika Slovenija
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Outside of Slovenia is the flag with the arms as the national flag in use,
Source, by: Flags of all Nations




State flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of all Nations






Merchant flag and state flag offshore,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)






Naval jack,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)




Flag of the President,
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)





1861–1919,
Flag of Goerz und Gradisca,
Source, by: Flags of the World




to 1918,
Flag of Istria,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1848–1919,
Flag of Carniola,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




1943–1945, Slovensko Domobranstvo,
Flag of the Home Guard,
ratio – ratio = 3:5,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)




1947–1991,
Flag of Slovenia in the SFR Yugoslavia,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: World Statesmen




The today’s flag of Slovenia was introduced on the 25th of June in 1991 on the occasion of the independence. It shows three horizontal stripes in white, blue and red with the coat of arms in the upper staff quadrant exactly between the white and the blue stripe. The colours of today's flag were last defined by the "Act on the Coat of Arms, Flag and National Anthem of the Republic of Slovenia and on the Slovenian National Flag" of 21st of October in 1994, but defined in an unknown, non-common colour space, the "SCOTDIC Code 777-Int'l Colour Codification System". This would make blue = N46 N722509, red = N23 N074014 and yellow = N6 N197512. Their mixture can be represented in RGB, so that one can narrow down reasonably suitable Pantone colour tones: Blue = Pantone 301, Red = Pantone 1788 and Yellow = 100% Y. Many Slavic nations create on the 19th century own flags – in context with a growing Slavic nationalism. Thereby played the Panslavism an important roll, a political movement of the 18th/19th century, which would unite all Slavs in one nation. The most Slavic nations however lived in this times under Austrian, Turkish or even German rule. The Panslavism saw in Russia a model, because the Russians were, apart from Serbia and Montenegro, the only free Slavic nation. In this way the colours of the Russian flag became to an idol of the Panslavists, and in the end to a colour's pattern in the designing of the flags of many Slavic nations. Those flags carried and carry except few exceptions the Russian colours white, blue and red as mutual attribute. From there this colour's combination is named "Panslavic Colours". In the year 1848 the Slowenes created their own flag in the colours white, blue and red. On the one hand they adoped a flag in the "Panslavian Colours" – an exact copy of the Russian flag, which became official in 1916. On the other hand in this way they took over the colours of the Duchy of Carniola. Carniola is the core of the today’s Slovenia. It was a crown-land of the Austria-Hungaryn monarchy, just like Istria and Goerz and Gradisca. After the end of Austria-Hungary, the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes was formed in the region, which was called Yugoslavia from 1929, to which the todays Slovenia belonged until 1991. In the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia, proclaimed by Tito in 1945, the South Slavic nations were able to use their national colors (mostly combinations of Panslavic colors) on their own flags again, in their own republics. However, because of the political system, a red star had to be used in the middle of the flag.
Source: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (D),
Flags of all Nations,
www.uradni-list.si


since 1991,
Coat of arms of Slovenia,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)

1945–1991,
Coat of arms of Slovenia,
Source: Romanm, vectorized by إيهاب-عبيد [GFDL
or CC-BY-SA-3.0], via Wikimedia Commons

The today’s coat of arms of Slovenia was created from the sculptor Marko Pogacnik and – ilke the flag – adoped in the year 1991. It shows in stylized shape the nature of the country. The three summits portray the mountain peaks of the Triglav Mountain (Dreizack, Trident), the highest mountain of the county. The both blue wave lines stand for the rivers Drave and Save, but even for the coast of the Adriatic Sea. The three six-pointed yellow stars above Triglav Mountain are borrowed from the coat of arms of the City of Celje (Cilli). They also stand for the historical important years of 1918 (independence from Austria-Hungary), 1945 (independence from the German Empire) and 1991 (independence from Yugoslavia).
Source: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (D)


since 1996,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

1991–1996,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
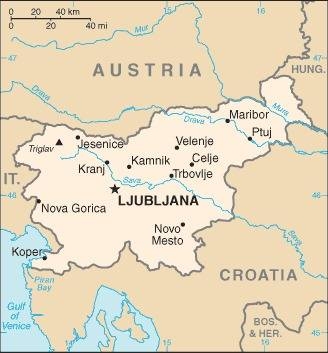
Source: CIA World Factbook
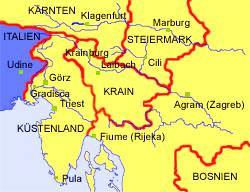
1880
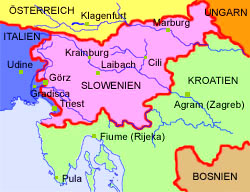
2005
The countries of the former Yugoslavia:
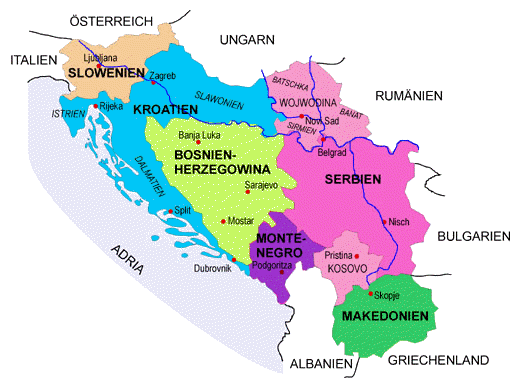
Map: Volker Preuß

Area: 7.827 square miles
Inhabitants: 2.100.000 (2022), davon 83% Slovenes, 2% Serbs, 1,8% Croats, furthermore Hungarians and Italians
Religions: 73% Roman Catholic, 3,7% Orthodox Christian, 3,7% Muslim, 18% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 268 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Ljubljana (German: Laibach), 285.604 inh. (2021)
official Language: Slovanian
other Languages: Italian, Hungarian, Serbian, Croatian, German
Currency since 1st of Jan. 2007: 1 Euro (EUR, €) = 100 Cent
Currency until 31st of Dec. 2006: 1 Tolar (SIT) = 100 Stotinov
Time Zone: GMT + 1 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D)

Antiquity · settlement by Illyrians
ca. 15 A.D. · the conquest of Krain (Krain = the core of Slovenia) by the Roman Empire is finished, comes to the Province of Pannonia Superior
395 · at the partition of the Roman Empire Dalmatia comes to the West Roman Empire (Rome)
476–489 · Krain belongs to the Empire of the Odoaker
489–553 · belongs to Empire of the Eastern Goth
6th cent. · settlement by Slavic tribes
569–598 · conquest by the Pannonian Avars
ca. 800 · the today's Krain becomes subjected by the Frankish Empire of the Carolingians, formation of the "Mark Krain", administration by the Margrave and Duke of Friaul
934 · the Mark Krain comes to Bavaria
976 · Krain comes to the Duchy of Carinthia
1394 · Krain (incl. Istria) becomes an own Duchy of the house of Habsburg
1797–1809 · French Revolutionar Wars, parts of Austria (Styria) become occupied by the French in 1797
1809 · Peace of Vienna, Austria loses Salzburg, the Inn Quarter, Western Galicia and parts of Eastern Galicia and cedes Istria, Trieste, Gorizia, Carniola, Carinthia, Croatia, and Dalmatia to France, which were merged in 1810 to the French "Illyrian Provinces"
1813 · Austria declares war on France (Napoléon)
1814/1815 · Congress of Vienna, realignment of Europe after the era Napoléon, the Empire of Austria (House of Habsburg) acquires back the in 1809 lost territories, they become merged to the Habsburg's Kingdom of Illyria, Carniola becomes a part of the Habsburg's Kingdom of Illyria, Dalmatia and Croatia become re-annexed to Hungary (under the Habsburgs, part of the Empire of Austria)
1848/1849 · revolution in Vienna, civil war between Hungarians and Croats, riotings in Prague, Mailand and Venice, as a result of that Emperor Ferdinand I. resigns and Franz Joseph I. of Habsburg becomes new Emperor, the riotings become suppressed and he enacts a new constitution: the titular hereditary territories of the Habsburgs in the Austrian Empire become converted to crown lands with their own Landtag (parliament), the Landtag of Dalmatia rejects the annexion to Croatia, the Kingdom of Dalmatia becomes an own crown land of the Austrian crown, Croatia and Slavonia become united to the "Kingdom of Croatia and Slavonia", which remains as a subsidiary country under the Hungarian crown, dissolution of the Kingdom of Illyria: division in the crown lands of Carniola, Carinthia, Littoral, Croatia and Slavonia and Dalmatia
1914–1918 · First World War, thereafter breakdown of the imperial-royal monarchy, disintegration of Austria-Hungary in national states
10th of September 1919 · Treaty of Peace of Saint-Germain after the First World War, Austria has to cede Krain and parts of Carinthia and Styria to the "Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes", since 1929 named Yugoslavia, Krain becomes the heartland of the Province of Drau (later Slovenia)
1939–1945 · Second World War, Yugoslavia is between 1941 and 1946 a location of a merciless partisan and civil war between communists (under J.P.Tito), republicans, monarchists and nationalists, the communists prevailed
6th of April 1941 · invasion of German and Italian troops
17th of April 1941 · capitulation of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia becomes dissolved: the King escape into the exile, some territories have to cede to neighbouring states (Macedonia, Kosovo, Banat and Slovenia), the Province of Bosnia-Hercegovina gets incorporated into Croatia, Croatia and Montenegro get independent, Serbia comes under German military administration, the District od Drau becomes partitioned between the German Empire (northern part) and Italy (southern part)
13th of October 1943 · capitulation of Italy, as a result of that occupys Germany among others also the southern part of the District od Drau, the "Province of Laibach / Ljubljanska Pokrajina"
19th of February in 1944 · founding of Federal Slovenia by the communist resistance
1945 · conquest and occupation of the area of todays Slovenia by Yugoslav partisans, expulsion and partially even assassination of the largest part of the in the country remained German civilian population
29th of November 1945 · proclamation of the "Federative People's Republic of Yugoslavia" by Tito
31st of January in 1946 · founding of the People's Republic of Slovenia
7th of April in 1963 · proclamation of the Socialist Republic of Slovenia (within communist Yugoslavia)
8th of March in 1990 · proclamation of the Republic of Slovenia
25th of June 1991 · Slovenia declares its independence from Yugoslavia
July–August 1991 · war aganist Yugoslavia
October 1991 · withdrawal of the Yugoslav troops
1992 · the European Community (EC) recognizes Slovenia as independent, Slovenia joines the UNO
2004 · Slovenia becomes a member of the European Union
1st of January 2007 · introduction of the Euro Currency
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (D)

The name of the country has its roots of course in the Slovenes, the most important ethnic group of the country. The word "Slovene" is derived from the Slavic word "slovit", what means "speak". The Slovens are in this way the "speaking". Noteworthy are the parallels to Slovakia, Slavonia and to the "Slavians" anyway.
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen


![]()























![]()
