zur deutschen Version, Flagge klicken oder tippen

- Dominion of Gibraltar
- possession of United Kingdom
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

since 1801,
Union Flag → quasi national flag,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)





since 1982,
National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World






since 1996,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




since 1999,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




since 1999,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




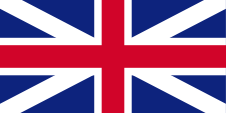
1704–1801,
Flag of United Kingdom (to 1707 of England),
Source, by:
Die Welt der Flaggen, Wikipedia (EN)






since 1801,
Union Flag → quasi national flag,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)






1864–1996,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of all Nations






1875–1923,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1923–1999,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1875–1982,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1982–1999,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Gibraltar came to United Kingdom in 1704 as a result of the Spanish War of
Succession. From this point onwards, individuals, citizens and also the
authorities represented their status as citizens or organs of the British
nation, embodied in the United Kingdom, by using the Union Jack, then called the
"Union Flag". At sea, the British merchant flag, the Red Ensign, was intended
for British citizens from 1864. In a few cases, the citizens of a colony were
authorised by the Admiralty to use their own Red Ensign with the colony's badge
at sea. Such permission was not granted to Gibraltar until 1996. Nevertheless, a
national flag was created in 1966 as a civic symbol that could be used by all
and was displayed alongside the Union Flag. It appears in the colours red and
white. The design of the flag is derived from the coat of arms of Gibraltar,
which showed the fortress of Gibraltar in the form of a stylised red castle on a
white background. The coat of arms was granted by Queen Isabella I. of Castile
in 1502. In 1982, the design of the flag was revised and officially introduced,
but it must be flown alongside the Union Flag, even abroad.
United
Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White
Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St.
George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the
real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant
of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use
by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in
the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
From 1865, the ships of the
colonial governments were allowed to use a Blue Ensign with a badge at the
flying end. The respective governments were to provide appropriate badges.
Merchant ships and seafaring privateers from colonies were only allowed to use a
Red Ensign with a badge if the British Admiralty had issued a corresponding
licence for that colony.
Such a badge was often a regional landscape
depiction on a disc, often showed ships, historical events or could simply be a
kind of logo. Very often a badge also contained the name of the country or a
motto. However, some possessions had a coat of arms from the beginning or were
given their own coat of arms over the years and the badge was abolished. To
ensure a largely uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of
arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disc in the size of the former
badges.
However, there were also exceptions, as some colonies dispensed
with this white disc and placed their coat of arms or even just the shield –
sometimes enlarged – directly on the bunting. As early as the 1940s, the white
disc was removed and the coat of arms was applied directly or enlarged. This
conversion process took place gradually, nowhere simultaneously and completely.
In some British possessions flags with the white disc are still in use today, in
others no longer and in some areas both variants exist side by side.
In
1875, an own "Blue Ensign" was introduced as the state flag at sea, a dark blue
bunting with a flag depiction – the British Union Jack – in the upper corner
(indicating the links to United Kingdom), which showed the coat of arms (with a
white castle on a red shield) on a white disc in the flying end of the flag as a
badge. In 1923 the white disc was removed, in 1999 the castle on the flag was
coloured in gold and the coat of arms was enlarged. In 1996, permission was
granted to use its own merchant flag ("Civil Ensign"). It is a so-called "Red
Ensign" and shows the traditional, historically handed down coat of arms of
Gibraltar, whereas the state flag at sea (the "Blue Ensign") shows a different
variant of the castle. As Gibraltar follows the British ensign and colour
system, the colours of the flag correspond to the spectrum specified by the
British Ministry of Defence in its publication "Flags of all Nations" (a service
regulation) for the following colours: Blue = pt 180 c, Red = pt 186 c, Deep
Yellow = pt 116 c.
Below the coat of arms there is a banner with the
motto "MONTIS INSIGNIA CALPE", which means "Of the mountain called Calpe". Calpe
is the old name of the Rock of Gibraltar. In ancient times, together with its
North African counterpart Abyla, it formed the so-called "Pillars of
Melkart/Heracles/Hercules", i.e. the Strait of Gibraltar.
The Governor's
flag was introduced in 1875 and is a standard design of older style, for all
Governors, Lieutenant-Governors, Commissioners, High Commissioners and other
officials holding a corresponding administrative office, provided that no newer
design is used. Within the wreath there is always the corresponding badge or
coat of arms, although in Gibraltar until 1999 the wreath was slightly smaller
than usual on these flags. In 1982, the image in the wreath was changed to show
the image of the flag with a white castle. In 1999, the wreath was enlarged and
the symbolism of the flag was adopted with a red castle and the coat of arms
motto was added in golden letters.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen, partial Jim Watt, Gibraltar, on 31st of March in 2002, Flags of the World


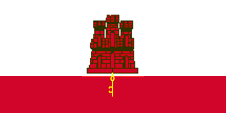
Coat of arms of Gibraltar,
Source, by: Escondites, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons

The coat of arms was awarded by document in 1502 to then Spanish Gibraltar. The document read as: "... we grant you as Arms an escutcheon on which two thirds of its upper part shall be a white field, in the said field is set a red castle, and underneath said castle, on the lower third of the escutcheon, which must be a red field, there must be a white line between the castle and said red field; on this field a golden key of the said castle shall hang by a chain." The origin of the castle has its roots in the heraldry of Castile, the most important and largest Spanish region, from which Great Britain acquired Gibraltar in the Spanish War of Succession.
Source:
partial, Jim Watt, Gibraltar, on 31st of March in 2002

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
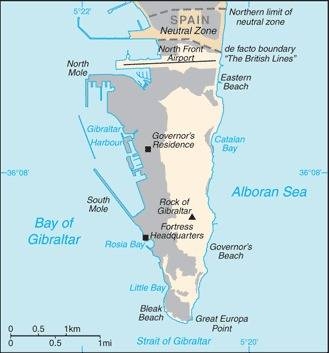
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 2,5 square miles
Inhabitants: 34.571 (2017), of which ancestry: 27 % British, 26 % Spanish, 19 % Italian, 11 % Portuguese, 8 % Maltese, 3 % Israeli
Religions: 78 % Catholic, 7 % Anglican, 4 % Muslim, 2 % Jewish, 2 % Hindu
Density of Population: 13.776 inh./sq.mi.
official Language: English
other Languages: Andalusian, Spanish
Currency: Gibraltar Pound (Gibr. £) = 100 Pence
Time Zone: GMT + 1 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D)

1704 · Gibraltar becomes British after the Spanish War of Sucession
1713 · Gibraltar becomes a British crown colony
1964 · United Kingdom grants internal self government
1968 · Gibraltar becomes Dominion
1969 · granting of extended internal self government
1969–1985 · closure of the border to Spain
2002 · referendum, turnout nearly 90 %, 99 % vote to remain under British rule
2009 · first Spanish state visit since 1704 by Foreign Minister Moratinos
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Discovery '97,
Wikipedia (DE)

The name "Gibraltar" is a shortened abrasion of the Arabic name for the rock. It was originally called "Djebel al Tariq" / "Mount of the Tarik", named after the Arab General Tarik Ibn Ziyad, who landed here in 711 and began with the Arab conquest of the Iberian Peninsula.
Source:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen


![]()










































