zur deutschen Version, Flagge klicken oder tippen

• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National, state and merchant flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN),
Corel Draw 4






Naval flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




since 2021,
Flag of the President,
ratio = 1:2,
Source: BaronJaguar, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons





1652–1660,
Flag of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen



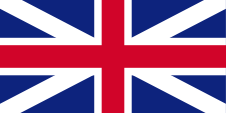
1660–1801,
Flag of United Kingdom (to 1707 of England),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen






1801–1966,
Union Flag → quasi national flag,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)






1864–1966,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of all Nations






1885–1966,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Sodacan, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons




1870–1966,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World, World Statesmen




1975–2021,
Flag of the Queen,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN),
Flags of all Nations,
Flags of the World




1966–2021,
Flag of the Governor General,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)



Windward Islands (1834–1885):

1903–1958, doubtful,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1885–1960,
Flag of the Governor-in-Chief,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



Federation of the West Indies (1958–1962):
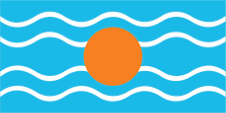
Flag of the Federation of the West Indies,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Governor General,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




The today's flag of Barbados was officially hoisted on 30th of November in 1966.
It was designed by G.W. Prescod and shows three vertical stripes in blue, yellow
and blue, as well as a black trident in the centre. The blue stripes symbolise
the sea and the sky, the yellow stripe in the middle the sandy beaches. The
three points of the trident symbolise three principles of government: Of the
people, with the people and for the people. The handle of the trident has been
deliberately omitted. This is intended to express the fact that Barbados has
overcome its colonial legacy. However, the trident also symbolises the people's
close ties to the sea.
Barbados still uses the British Ensign system
today. This points to the links with United Kingdom, as the naval flag is a
white ensign, a white flag with a continuous red St George's cross and with the
national flag in the top corner.
The colours of the flag are defined by
law in the old British Standard Colour Code: Ultramarine - BCC 148, Gold - BS
O/002. In practice, the colours are based on the colour specifications of the
British Admiralty, interpreted today as: Blue = Pantone 280 C, Deep Yellow =
Pantone 116 C, Red = Pantone 186 C.
From the time the territory became a
British possession, individuals, citizens and also the authorities represented
their status as citizens or organs of the British nation, embodied in the United
Kingdom, through the use of the Union Jack, then called the "Union Flag". At
sea, the British merchant flag, the Red Ensign, was intended for British
citizens from 1864. In a few cases, the citizens of a colony were authorised by
the Admiralty to use their own Red Ensign with the colony's badge at sea. The
Union Jack in the top corner of these flags signalled the connection to United
Kingdom.
Barbados originally belonged to the British colony of the
Windward Islands until 1885, was then a dissociated own colony, joined the West
Indies Federation in 1958 and became a dissociated own colony again in 1962.
United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly
the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red
St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the
flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil
flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff
quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag
for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the
Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
From 1865, the ships
of the colonial governments were allowed to use a Blue Ensign with a badge at
the flying end. The respective governments were to provide appropriate badges.
Merchant ships and seafaring privateers from colonies were only allowed to use a
Red Ensign with a badge if the British Admiralty had issued a corresponding
licence for that colony. Such a badge was often a regional landscape depiction
on a disc, often showed ships, historical events or could simply be a kind of
logo. Very often a badge also contained the name of the country or a motto.
However, some possessions had a coat of arms from the beginning or were given
their own coat of arms over the years and the badge was abolished. To ensure a
largely uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and
other symbols were displayed on a white disc in the size of the former badges.
However, there were also exceptions, as some colonies dispensed with this white
disc and placed their coat of arms or even just the shield – sometimes enlarged
– directly on the bunting. As early as the 1940s, the white disc was removed and
the coat of arms was applied directly or enlarged. This conversion process took
place gradually, nowhere simultaneously and completely. In some British
possessions flags with the white disc are still in use today, in others no
longer and in some areas both variants exist side by side.
The territory
was part of the British Colony of the Windward Islands from 1834 to 1885, a
federal colony consisting of individual sub-areas, sub-colonies or islands.
These individual colonies often had their own flags from around 1865, also known
as "Blue Ensigns" with their own badge for use by the governments of these
colonies. The overarching political entity of the British Windward Islands most
likely did not have an additional Blue Ensign of its own, but its own badge.
This badge was created in 1886 and showed an heraldic shield divided into four
parts with the colours red, yellow, green and white, surrounded by a white belt
with the inscription "Governor in Chief, Windward Islands", with the British
crown above. Below is a white banner with the motto of the islands: "i pede
fausto" → "Walk with a blessed foot". In 1903, the design of the crown was
changed slightly (to the Tudor crown). The Governor of Barbados was always also
the Governor-in-Chief of the colony of the British Windward Islands. The
Governor-in-Chief used the Windward Islands badge on his flag after all. He was
represented locally by a governor in the associated sub-territory, sub-colony or
island. The federal colony ceased to exist when it was incorporated into the
Federation of the West Indies, led by a Governor-General. Locally, in the
associated sub-territory, sub-colony or island, the highest representative of
the Crown retained his rank. He remained an administrator or governor. The local
flags (e.g. blue or red ensigns, i.e. separate state or merchant flags) have
been retained.
Barbados was given its own badge in 1885, as the island was no longer part of
the Windward Islands but had become a dissociated own colony. The badge showed
on a disc Britannia riding two seahorses with a trident in her right hand. The
tip of the trident now appears in the centre stripe of the today's flag. Also in
1885, an own "Blue Ensign" was introduced as the state flag at sea, a dark blue
bunting with a flag depiction – the British Union Jack – in the upper corner,
which showed the badge in the flying end of the flag.
From 1958 to 1962
the territory was also part of the British colony "Federation of the West
Indies". This political project was an attempt to unify the administration and
to create a state modelled on Canada, but also to counteract the independence
efforts of the associated islands and colonies. However, jealousies arose
between the large and small islands and even led to open dispute. The flag of
the "Federation of the West Indies" was a light blue flag with four horizontal
white wavy lines and a golden disc in the middle. It symbolized the sun over the
Caribbean Sea. There is some doubt about the color of the blue; it is often
assumed to be the usual British heraldry blue. However, a contemporary
description calls it an "imperial blue" which would be light blue and many
contemporary prints also show this light blue.
In 1961, Barbados was
granted internal self-government by United Kingdom and became an autonomous
state associated with United Kingdom. Independence was granted by United Kingdom
on 30th of November in 1966. In this context, the current flag was introduced.
Source: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Wappen, Translator of the English text (partial): Joachim Nuthack


Coat of arms of Barbados,
Source:
Flaggen und Wappen,
Corel Draw 4

The coat of arms of Barbados was awarded by the British Queen Elisabeth II on the 21st of December 1966, and replaced the badge. It shows in a golden shield an uprooted "bearded fig tree". The name of the island is derived from this tree. The Spanish word barbados means bearded. In the upper sections of the blazon are two red orchids. This species of orchids has the name "Red Pride of Barbados", and is the national plant. The shield carries a helmet with yellow-red blankets. From there an arm of a native reaches out. Its hand holds two sugarcane stems. Shield holders are a dolphin and a pelican. They stand for the fishing and the fauna of the island. Underneath a golden banner with the motto of the land: "Pride and Industry".
Source: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Wappen


since 1981,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
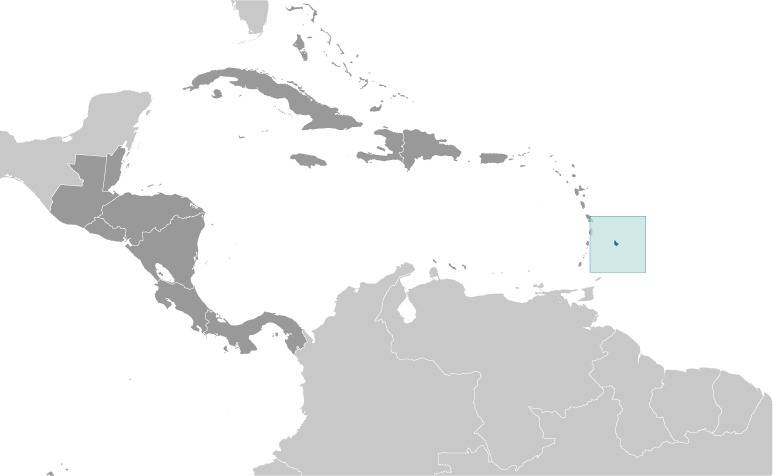
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
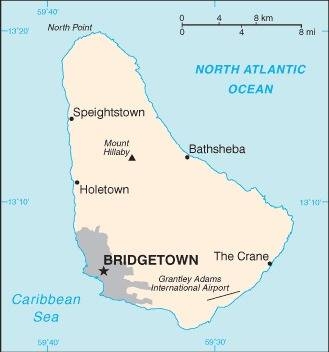
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 166 square miles
Inhabitants: 278.000 (2010), thereof 92% of African descent, 3% Mulattos, 3% Europeans
Religions: 66% Protestant, 4% Roman Catholic, 5% other Christian
Density of Population: 1.674 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Bridgetown, 110.000 inh. (2014)
official Language: English
Currency: 1 Barbados-Dollar (BBD, B$, BDS$) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT – 4 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
CIA World Factbook

1519 · discovered by Spain, named "Isla de los Barbados"
1536 · re-discovery and appropriation by the Portuguese seafarer Pedro a Campos, he names the island "Ilha Barbudos"
1626 · appropriation by England
1627 · initial english colonization
1663 · english crown colony
1834–1885 · part of the British Colony of the Windward Islands
1958–1962 · part of the British Colony of the "Federation of the West Indies"
1961 · internal self government
30th of November 1966 · the United Kingdom grants independence
September 2020 · the government announces the end of the monarchy and the transformation of the state into a republic for November 2021
1st of December in 2021 · the British Queen is deposed as head of state and the constitutional monarchy ends, the Governor General of Barbados becomes President of the Republic of Barbados after her election on 20th of October in 2021, the country remains in the Commonwealth of Nations
Source: Wikipedia (D),
Wikipedia (EN),
World Statesmen

The name "Barbados" means translated "bearded". Obviously, the Spaniards, when they gave the island its name, had been inspired by the fig trees that grow here with aerial roots.
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen


![]()








































